Page 40 - 02
P. 40
40 Y.A. SOYADI, Y.A. SOYADI, Y.A. SOYADI ve Y.A. SOYADI
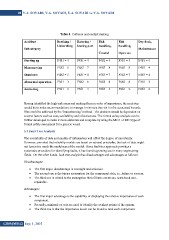
Table 4. Collision and contact ranking
Accident Berthing / Entering / Fish Fish Dry dock,
Subcategory handling, Maintenance
Unberthing leaving port handling, Open sea
Starting up F4S1 = 4
Manoeuvring Coastal F3S1 = 3 F4S1 = 4
Shutdown F6S3 = 8 F4S1 = 4
Abnormal operation F4S1 = 4 F4S1 = 4 F4S1 = 4 F5S3 = 7 F3S1 = 3
Anchoring F6S3 = 8 F2S1 = 2
F5S2 = 6 F6S2 = 7 F6S3 = 8 F2S1 = 2
F4S2 = 5 F4S1 = 4 F5S3 = 7
F3S1 = 3 F5S2 = 6 F6S3 = 8
F5S1 = 5 F3S1 = 3 F3S1 = 3
Having identified the high-risk areas and ranking them in order of importance, the next step
would be to make recommendations to manage / minimize the risk for the associated hazards.
This could be achieved by the „brainstorming‟ method. The decision would be dependent on
several factors such as cost, availability and effectiveness. The formal safety analysis can be
further developed to make it more elaborate and complete by using the MCA or IMO type of
formal safety assessment for a generic vessel.
5.1 Fault Tree Analysis
The availability of data and quality of information will affect the degree of uncertainty.
However, provided that reliabilty models are based on rational principles, the lack of data might
not lessen too much the usefulness of the model. Since fault tree approach provides a
systematic procedure for identifying faults, it has found a growing use in many engineering
fields. On the other hands, fault tree analysis has disadvantages and advantages as follows:
Disadvantages:
The first major disadvantage is oversight and omission.
The second one is the binary assumption for the component state, i.e. failure or success.
The third one is related to the assumption that all basic events are considered non-
repairable.
Advantages:
The first major advantage is the capability of displaying the relative importance of each
component.
Secondly, minimal cut sets are used to identify the weakest points of the system.
The third one is that the importance levels can be found to rank each component.
GiDB|DERGi Sayı 1, 2015