Page 32 - 07
P. 32
30 A. TUNÇER, G.T. TAYYAR and Y. ÜNSAN
Figure 5.6 PWM [21]
5.5 PID
Desired output values can be adjusted by several methods in closed-loop systems. PID is the
majority of the control types in the industrial applications. PID stands for Proportional, Integral
and Derivative. Proportional path multiplies the error by a constant (Kp) while the integral path
multiplies the error with a constant (Ki) then integrates it and the derivative path multiplies the
error with a constant (Kd) then differentiates it.
These paths can be used alone as; P, I or D. Or used as PI, PD or PID according to the required
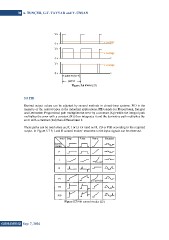
output. In Figure 5.7 P, I and D control modes’ treatment to the input signals can be observed.
Figure 5.7 PID control modes [22]
GiDB|DERGi Sayı 7, 2016