Page 38 - 07
P. 38
FAULT TOLERANT CONTROL OF ROTOR SWING 35
STABILIZER SYSTEM USING FMEA METHOD
- Design a reconfiguration mechanism which guides by any means necessary to recover,
of the preliminary fault system performance,
- Value the time which is restricted for the FDD and for the control system
reconfiguration.
Figure 1. Basic scheme of a fault tolerant control system [1].
Fault diagnosis detects the faults in the system and isolates them as much as possible and all the
variables, system status, output variables, and subsequent fault system models are required to be
forecasted on line in real time. Reconfigurable controller is planned to continue stabilization,
essential dynamic performance and steady-state performance on the basis of information
coming from subsequent fault system.
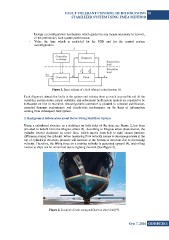
3. Background Information about Rotor Swing Stabilizer System
Using a cylindrical structure as a stabilizer on both sides of the ship, see Figure 2, has been
provided to benefit from the Magnus effect [3]. According to Magnus effect phenomenon, the
cylinder rotated clockwise in water flow, which moves from left to right causes pressure
difference around the cylinder. When increasing flow velocity causes to decrease pressure at the
top of cylindrical structure, pressure will increase at the bottom of structure due to decreasing
velocity. Therefore, the lifting force on a rotating cylinder is generated upward [4], and rolling
motion at ships can be minimized due to righting moment (See Figure 3).
Figure 2. Location of rotor swing stabilizer on ship’s hull [9].
Sayı 7, 2016 GiDB|DERGi