Page 50 - 07
P. 50
FAULT TOLERANT CONTROL OF ROTOR SWING 47
STABILIZER SYSTEM USING FMEA METHOD
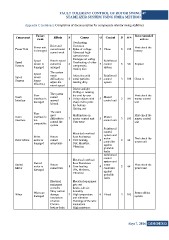
Appendix C (continue): Completion of documentation for components of rotor swing stabilizer
Component Failure Effects S Causes O Control D RPN Recommended
mode actions
Overheating
Power Unit Power unit Drive and Corrosion 3 None 8 192 First check the
is damaged swivel motor 8 Spike of voltage battery
cannot work
Abnormal high-
current power
Speed Speed Rotor's speed 6 Damages on wiring 3 Reinforced 5 90 Replace
Sensors sensor is cannot be Overheating of other control
damaged arranged components system
Battery dies
Speed Speed The system Attraction with Reinforced
Sensors sensor meets 6 metal particles
losses difficulty to 6 control 3 108 Clean it
efficiency adjust the Getting dirty
rotor's speed system
Direct sunlight
Users User The system Pulling or twisting 5 Master 2 First check the
Interface interface is cannot the cord by user control unit 80 master control
damaged opened 8 Using objects with
/closed sharp end to press unit
the buttons
Getting wet
Users User The users Malfunction on 5 Master 3 First check the
Interface interface is meet 7 master control unit control unit 105 master control
not difficulty to
compatible control the User error unit
system
Reinforced
Electrical overload control
Low Resistance
Drive Rotors 8 Over heating system and
motor is cannot Dirt, Moisture,
Drive Motor damaged open/close Vibration 4 motor 2 64 First check the
controller power unit
against
probable
faults
Reinforced
Electrical overload control
Low Resistance
Swivel 8 Over heating system and
motor is Dirt, Moisture,
Swivel damaged Rotors Vibration 4 motor 2 64 First check the
Motor cannot turn controller power unit
against
probable
faults
Electrical Electrical equipment
equipment gets wet
corrodes Leaks, salt air,
Wires are Stray current humidity Power off the
damaged system
Wires damage 9 High temperature 6 Visual 3 162
Insulations and vibration
of wires Paintings of the wire
Chronic insulations
battery drain High resistance
Sayı 7, 2016 GiDB|DERGi